Types of Power in a SoC Design
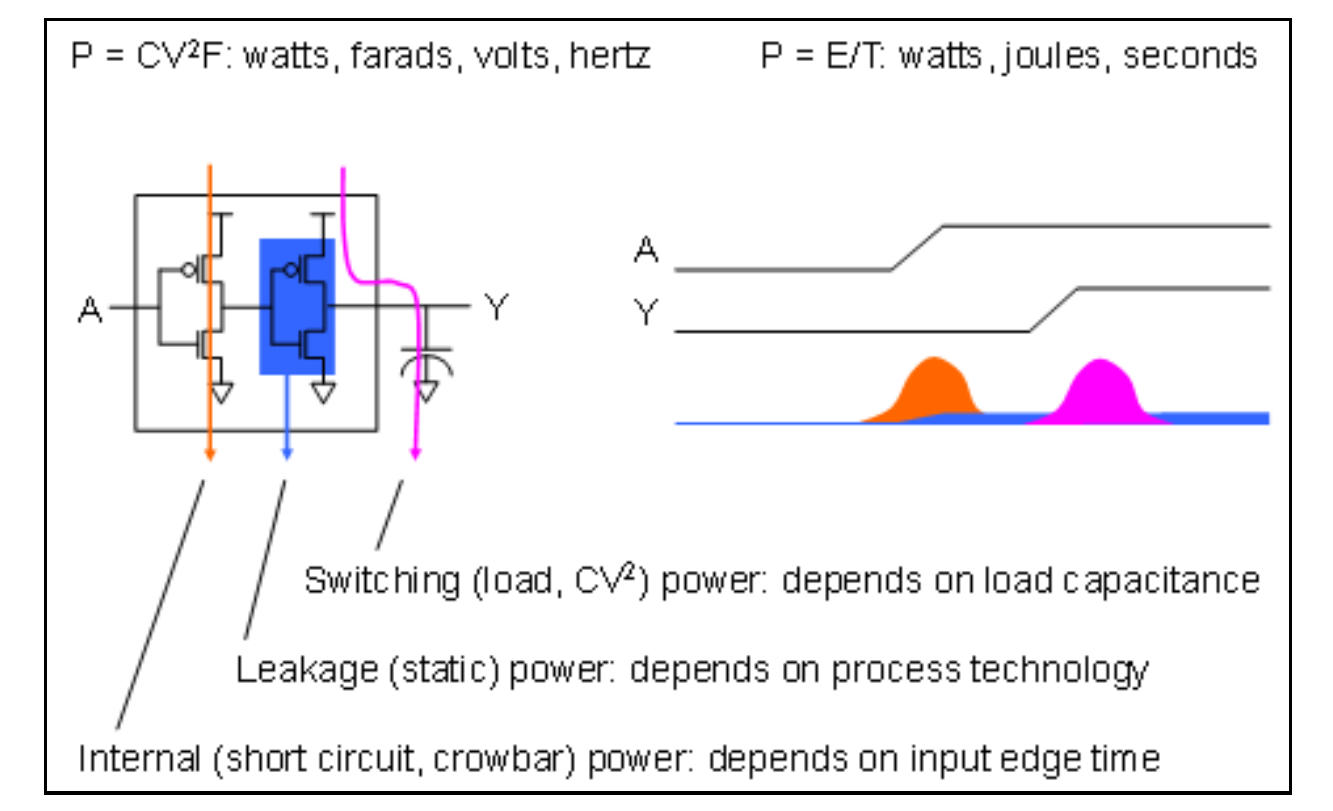
Dynamic Power
- Switching Power: This is the power spent charging and discharging the capacitance of the output net; it is also called load power or CV2 power. Since switching power is a function of switching activity and load capacitance, it is data dependent.
- Internal Power (Short Circuit Power/Crowbar Power): This is the power dissipated inside the gate when switching. This power is also called short power or crowbar power.
Static Power
- Static power is the power consumed by a device when no signals are changing values. Since static power consumption is primarily caused by leakage, in CMOS devices, Static Power is also known as Leakage Power. This is the power dissipated whenever the device is powered, regardless of activity; there are several sources of leakage power but they are all lumped together into a single value for modeling purposes. The amount of leakge power dissipated by a gate can depend on the logic state of the inputs. This is called “state-dependent leakage power“; most tools can model this if it is described in the library data.
Power Components
- Combinational: Combinational cell and a net driven by the combinational cell
- Sequential: Registers, Latch, ICG and the output net of the sequential logic
- Clock: Clock network
- IO: IO pad cell and the output net of the IO cell
- Memory: Memory and the output nets of the memory cell
- Macrocell:
- Blackbox: